Django | Set up environment variables in Django
1. Install Django Environ
In your terminal, inside the project directory, type:
$ pip install django-environ
2. Import environ in settings.py
import environ
3. Initialise environ
Below is your import in settings.py:
import environ # Initialise environment variables env = environ.Env() environ.Env.read_env()
4. Create your .env file
In the same directory as settings.py, create a file called ‘.env’
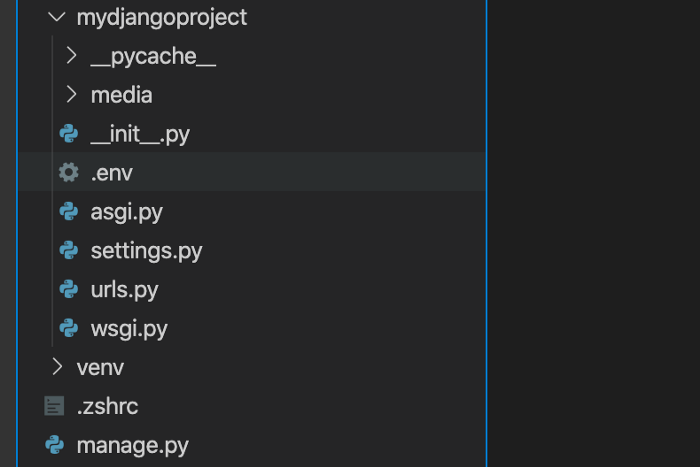
5. Declare your environment variables in .env
Make sure you don’t use quotations around strings.
SECRET_KEY=h^z13$qr_s_wd65@gnj7a=xs7t05$w7q8!x_8zsld# DATABASE_NAME=postgresdatabase DATABASE_USER=alice DATABASE_PASS=supersecretpassword
6. Replace all references to your environment variables in settings.py
DATABASES = {
‘default’: {
‘ENGINE’: ‘django.db.backends.postgresql_psycopg2’,
‘NAME’: env(‘DATABASE_NAME’),
‘USER’: env(‘DATABASE_USER’),
‘PASSWORD’: env(‘DATABASE_PASS’),
}
}
And
SECRET_KEY = env(‘SECRET_KEY’)
Tips and Tricks
Python In-place swapping of two numbers
Python | In-place swapping of two numbers
>>> a, b = 10, 20
>>> print(a, b)
10 20
>>> a, b = b, a
>>> print(a, b)
20 10
Reversing a String in Python
Python | Reversing a String
>>> x = 'PythonWorld'
>>> print(x[: : -1])
dlroWnohtyP
Python join all items of a list to convert into a single string
Python | Join all items of a list to convert into a single string
>>> x = ["Python", "Online", "Training"]
>>> print(" ".join(x))
Python Online Training
python return multiple values from functions
Python | Return multiple values from functions
>>> def A():
return 2, 3, 4
>>> a, b, c = A()
>>> print(a, b, c)
2 3 4
Python Print String N times
Python | Print String N times
>>> s = 'Python'
>>> n = 5
>>> print(s * n)
PythonPythonPythonPythonPython